Regular eye examinations are essential for maintaining good eye health and ensuring optimal vision. Whether it’s your first visit or a routine check-up, knowing what to expect can make the experience smoother and less intimidating. Here’s a detailed look at what happens during a typical eye examination.
1. Patient History and Preliminary Information
Your eye exam usually begins with a discussion about your medical history and any vision issues you may be experiencing. The optometrist or ophthalmologist will ask about:
- Current symptoms: Blurry vision, headaches, eye strain, etc.
- Medical history: Any past eye conditions or surgeries, general health issues like diabetes or hypertension.
- Family history: Eye diseases like glaucoma or macular degeneration.
- Lifestyle factors: Your occupation, screen time, and hobbies that may affect your vision.
2. Visual Acuity Test
The next step is to measure how well you see at various distances. This is typically done using an eye chart:
- Snellen Chart: You’ll be asked to read letters of decreasing size from a distance of 6 metres. This measures your distance vision.
- Near Vision Test: You’ll read from a small card held at reading distance to assess your near vision.
3. Refraction Assessment
To determine the exact prescription for glasses or contact lenses, a refraction test is conducted. The optometrist will use a phoropter, a device with multiple lenses, to determine which lens combination gives you the clearest vision:
- Manual Refraction: You’ll look through the phoropter and respond to the optometrist’s prompts, such as “Which is better, lens one or lens two?”
- Autorefractor: This machine estimates your prescription by measuring how light is changed as it enters your eye.
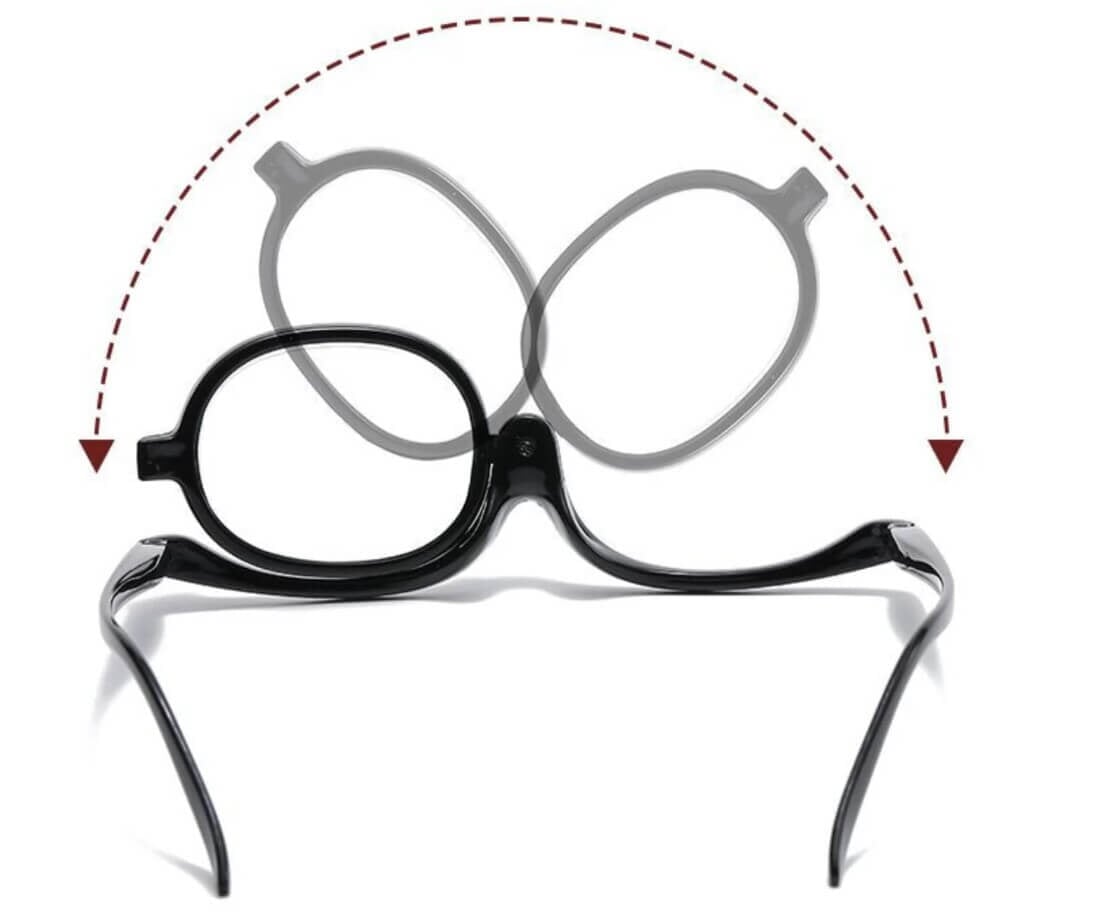
4. Eye Muscle Test
To assess the muscles that control eye movement, the optometrist will have you follow a moving object (like a pen or a small light) with your eyes. This checks for any weakness or coordination issues in your eye muscles.
5. Pupil Reaction Test
Your pupils’ responses to light and close objects are examined. The optometrist will shine a light in your eyes and observe how your pupils react, checking for signs of neurological issues.
6. Slit Lamp Examination
A slit lamp is a powerful microscope with a bright light used to examine the front parts of your eye, including the eyelids, cornea, iris, and lens:
- Fluorescein Dye Test: Sometimes a dye is used to highlight abnormalities on the surface of your eye.
- Detailed Examination: The slit lamp helps detect conditions like cataracts, corneal injuries, and other eye diseases.
7. Intraocular Pressure Measurement
To screen for glaucoma, the pressure inside your eye (intraocular pressure) is measured:
- Tonometry: The optometrist may use a puff of air or a special device that gently touches the eye. Numbing drops are used to make this comfortable.
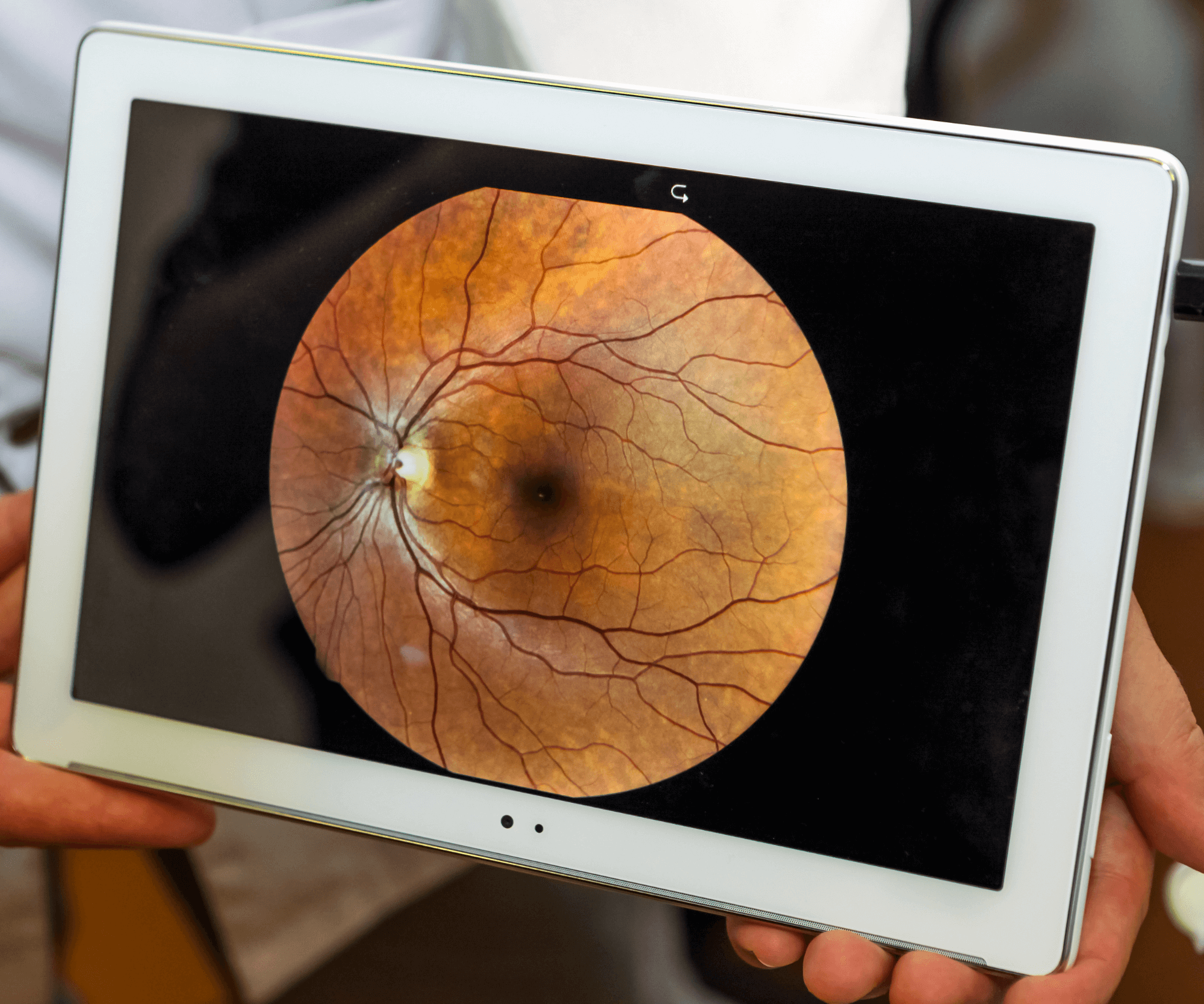
8. Retinal Examination
The health of your retina, optic nerve, and blood vessels is crucial for overall eye health:
- Ophthalmoscopy: Using an ophthalmoscope, the optometrist looks through your pupil to examine the retina and optic nerve.
- Dilated Eye Exam: Eye drops are used to widen (dilate) your pupils for a more detailed view. This can cause blurred vision and light sensitivity for a few hours.
9. Additional Tests
Depending on your age, health, and results of the initial tests, additional assessments may be performed:
- Visual Field Test: Measures your peripheral vision.
- Colour Vision Test: Checks for colour blindness.
- Digital Ocular Imaging: A wide view photograph of the retina.
10. Discussion and Recommendations
After all the tests, the optometrist will discuss the results with you:
- Prescription: If needed, a prescription for glasses or contact lenses will be provided.
- Diagnosis: Any eye conditions will be explained, and treatment options will be discussed.
- Preventive Measures: Tips for maintaining eye health, like proper nutrition, UV protection, and screen time management, will be shared.
Conclusion
Regular eye exams are vital for detecting and treating eye conditions early, ensuring that you maintain good vision and overall eye health. By understanding what happens during an eye examination, you can approach your appointment with confidence and take an active role in preserving your sight.
—
Remember: Always schedule regular eye check-ups, especially if you notice any changes in your vision or have risk factors for eye diseases. Your eyes are an essential part of your health, and taking care of them should be a priority.